The C++ Application Plugin provides the tasks, configurations and conventions for a building C++ application.
Usage
plugins {
`cpp-application`
}plugins {
id 'cpp-application'
}Build variants
The C++ Application Plugin understands the following dimensions. Read the introduction to build variants for more information.
- Build types - always either debug or release
-
The build type controls the debuggability as well as the optimization of the generated binaries.
-
debug- Generate debug symbols and don’t optimized the binary -
release- Generate debug symbols and optimize, but extract the debug symbols from the binary
-
- Target machines - defaults to the build host
-
The target machine expresses which machines the application expects to run. A target machine is identified by its operating system and architecture. Gradle uses the target machine to decide which tool chain to choose based on availability on the host machine.
The target machine can be configured as follows:
application {
targetMachines = listOf(machines.linux.x86_64,
machines.windows.x86, machines.windows.x86_64,
machines.macOS.x86_64)
}application {
targetMachines = [
machines.linux.x86_64,
machines.windows.x86, machines.windows.x86_64,
machines.macOS.x86_64
]
}Tasks
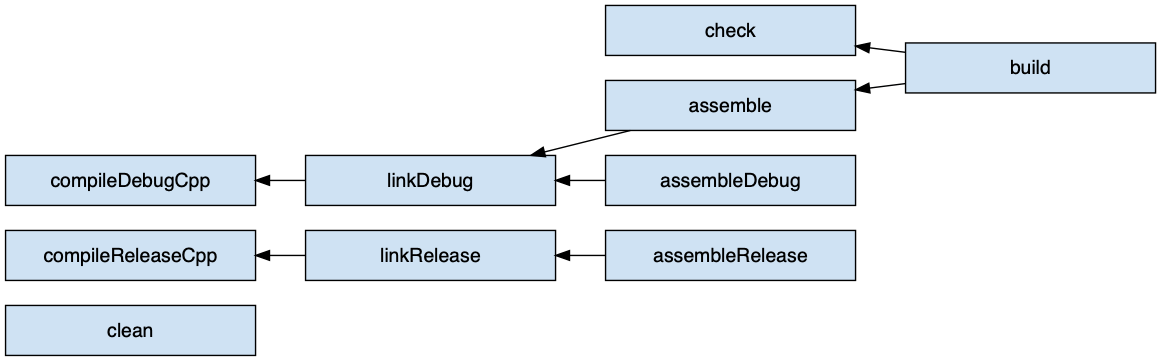
The following diagram shows the relationships between tasks added by this plugin.
Variant-dependent Tasks
The C++ Application Plugin creates tasks based on the variants of the application component. Read the introduction to build variants for more information. The following diagram shows the relationship between variant-dependent tasks.
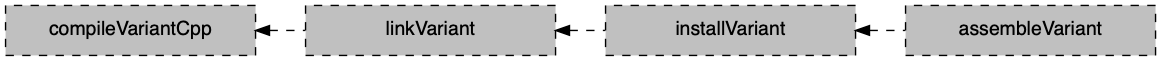
compileVariantCpp(e.g.compileDebugCppandcompileReleaseCpp) - CppCompile-
Depends on: All tasks that contribute source files to the compilation :: Compiles C++ source files using the selected compiler.
linkVariant(e.g.linkDebugandlinkRelease) - LinkExecutable-
Depends on: All tasks which contribute to the link executable, including
linkVariantandcreateVarianttasks from projects that are resolved via project dependencies :: Links executable from compiled object files using the selected linker. installVariant(e.g.installDebugandinstallRelease) - InstallExecutable-
Depends on:
linkVariantand all tasks which contribute to the runtime of the executable, includinglinkVarianttasks from projects that are resolved via project dependencies :: Installs the executable and all of it’s runtime dependencies for easy execution. assembleVariant(e.g.assembleDebugandassembleRelease) - Task (lifecycle)-
Depends on:
linkVariant:: Aggregates tasks that assemble the specific variant of this application.
Lifecycle Tasks
The C++ Application Plugin attaches some of its tasks to the standard lifecycle tasks documented in the Base Plugin chapter - which the C++ Application Plugin applies automatically:
assemble- Task (lifecycle)-
Depends on:
linkDebug:: Aggregate task that assembles the debug variant of the application for the current host (if present) in the project. This task is added by the Base Plugin. check- Task (lifecycle)-
Aggregate task that performs verification tasks, such as running the tests. Some plugins add their own verification task to
check. For example, the C++ Unit Test Plugin attaches a task to this lifecycle task to run tests. This task is added by the Base Plugin. build- Task (lifecycle)-
Depends on:
check,assemble:: Aggregate tasks that perform a full build of the project. This task is added by the Base Plugin. clean- Delete-
Deletes the build directory and everything in it, i.e. the path specified by the
layout.buildDirectoryproject property. This task is added by the Base Plugin.
Dependency management
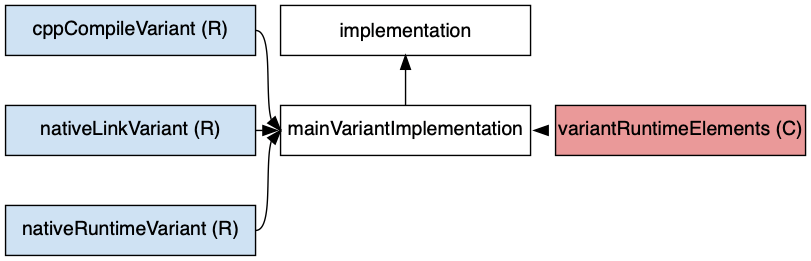
Just like the tasks created by the C++ Application Plugin, multiple configurations are created based on the variants of the application component. Read the introduction to build variants for more information. The following graph describes the configurations added by the C++ Application Plugin:
-
The configurations in white are the ones a user should use to declare dependencies
-
The configurations in pink, also known as consumable denoted by (C), are the ones used when a component runs against the library
-
The configurations in blue, also known as resolvable denoted by (R), are internal to the component, for its own use
The following configurations are used to declare dependencies:
implementation-
Used for declaring implementation dependencies for all variants of the main component. This is where you should declare dependencies of any variants.
mainVariantImplementation(e.g.mainDebugImplementationandmainReleaseImplementation) extendsimplementation-
Used for declaring implementation dependencies for a specific variant of the main component. This is where you should declare dependencies of the specific variant.
The following configurations are used by downstream consumers that depend on the application component:
variantRuntimeElements(e.g.debugRuntimeElementsandreleaseRuntimeElements) extends `mainVariantImplementation-
Used for executing the application. This configuration is meant to be used by consumers, to retrieve all the elements necessary to run the application.
The following configurations are used by the application itself:
cppCompileVariant(e.g.cppCompileDebugandcppCompileRelease) extendsmainVariantImplementation-
Used for compiling the application. This configuration contains the compile include roots of the application and is therefore used when invoking the C++ compiler to compile it.
nativeLinkVariant(e.g.nativeLinkDebugandnativeLinkRelease) extendsmainVariantImplementation-
Used for linking the application. This configuration contains the libraries of the application and is therefore used when invoking the C++ linker to link it.
nativeRuntimeVariant(e.g.nativeRuntimeDebugandnativeRuntimeRelease) extendsmainVariantImplementation-
Used for executing the application. This configuration contains the runtime libraries of the application.
Conventions
The C++ Application Plugin adds conventions for sources and tasks, shown below.
Project layout
The C++ Application Plugin assumes the project layout shown below. None of these directories need to exist or have anything in them. The C++ Application Plugin will compile whatever it finds and ignore anything missing.
src/main/cpp-
C++ source with extension of
.cpp,.c++or.cc src/main/headers-
Headers - headers needed to compile the application
You configure the project layout by configuring the source and privateHeaders respectively on the application script block.
compileVariantCpp Task
The C++ Application Plugin adds a CppCompile instance for each variant of the application component to build (e.g. compileDebugCpp and compileReleaseCpp).
Read the introduction to build variants for more information.
Some of the most common configuration options are shown below.
| compilerArgs |
[] |
| debuggable |
|
| includes |
|
| macros |
[:] |
| objectFileDir |
|
| optimized |
|
| positionIndependentCode |
|
| source |
|
| systemIncludes |
derived from the tool chain |
| targetPlatform |
derived from the |
| toolChain |
linkVariant Task
The C++ Application Plugin adds a LinkExecutable instance for each variant of the application — e.g. linkDebug and linkRelease.
Read the introduction to build variants for more information.
Some of the most common configuration options are shown below.
| debuggable |
|
| libs |
|
| linkedFile |
|
| linkerArgs |
[] |
| source |
|
| targetPlatform |
derived from the |
| toolChain |
installVariant Task
The C++ Application Plugin adds a InstallExecutable instance for each variant of the test component — e.g. installDebug and installRelease.
Read the introduction to build variants for more information.
There is no need to configure any properties on the task.