Build Lifecycle
The build lifecycle is the sequence of phases Gradle executes to turn your build scripts into completed work, from initializing the build environment to configuring projects and finally executing tasks.
Build Phases
A Gradle build has three distinct phases.

Gradle runs these phases in order:
| Phase 1. Initialization | Phase 2. Configuration | Phase 3. Execution |
|---|---|---|
- Detects the settings file |
- Evaluates the build files of every project participating in the build |
- Schedules and executes the selected tasks |
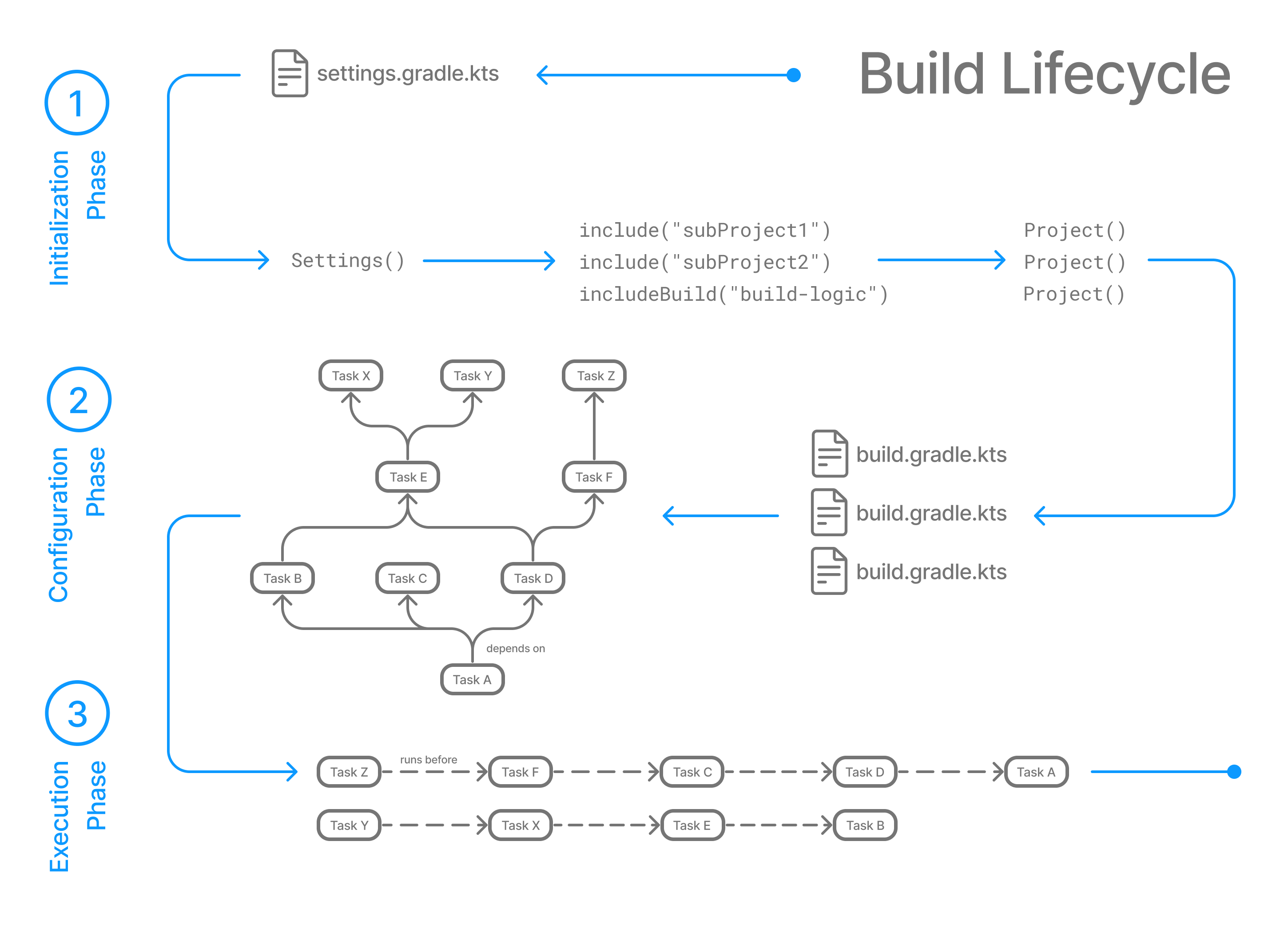
The following example shows which parts of settings and build files correspond to various build phases:
rootProject.name = "basic"
println("This is executed during the initialization phase.")println("This is executed during the configuration phase.")
tasks.register("configured") {
println("This is also executed during the configuration phase, because :configured is used in the build.")
}
tasks.register("test") {
doLast {
println("This is executed during the execution phase.")
}
}
tasks.register("testBoth") {
doFirst {
println("This is executed first during the execution phase.")
}
doLast {
println("This is executed last during the execution phase.")
}
println("This is executed during the configuration phase as well, because :testBoth is used in the build.")
}rootProject.name = 'basic'
println 'This is executed during the initialization phase.'println 'This is executed during the configuration phase.'
tasks.register('configured') {
println 'This is also executed during the configuration phase, because :configured is used in the build.'
}
tasks.register('test') {
doLast {
println 'This is executed during the execution phase.'
}
}
tasks.register('testBoth') {
doFirst {
println 'This is executed first during the execution phase.'
}
doLast {
println 'This is executed last during the execution phase.'
}
println 'This is executed during the configuration phase as well, because :testBoth is used in the build.'
}The following command executes the test and testBoth tasks specified above.
Because Gradle only configures requested tasks and their dependencies, the configured task never configures:
> gradle test testBoth
This is executed during the initialization phase.
> Configure project :
This is executed during the configuration phase.
This is executed during the configuration phase as well, because :testBoth is used in the build.
> Task :test
This is executed during the execution phase.
> Task :testBoth
This is executed first during the execution phase.
This is executed last during the execution phase.
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 0s
2 actionable tasks: 2 executed> gradle test testBoth
This is executed during the initialization phase.
> Configure project :
This is executed during the configuration phase.
This is executed during the configuration phase as well, because :testBoth is used in the build.
> Task :test
This is executed during the execution phase.
> Task :testBoth
This is executed first during the execution phase.
This is executed last during the execution phase.
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 0s
2 actionable tasks: 2 executedPhase 1. Initialization
In the initialization phase, Gradle detects the set of projects (root and subprojects) and included builds participating in the build.
Gradle first evaluates the settings file, settings.gradle(.kts), and instantiates a Settings object.
Then, Gradle instantiates Project object instances for each project included in the build (using includeBuild() or include() in the settings file).
Phase 2. Configuration
In the configuration phase, Gradle adds tasks and other properties to the projects found by the initialization phase.
Gradle constructs the task graph by understanding the dependencies between tasks.
Phase 3. Execution
In the execution phase, Gradle runs tasks.
Gradle uses the task execution graphs generated by the configuration phase to determine which tasks to execute. Gradle can execute tasks in parallel.
Task Graphs
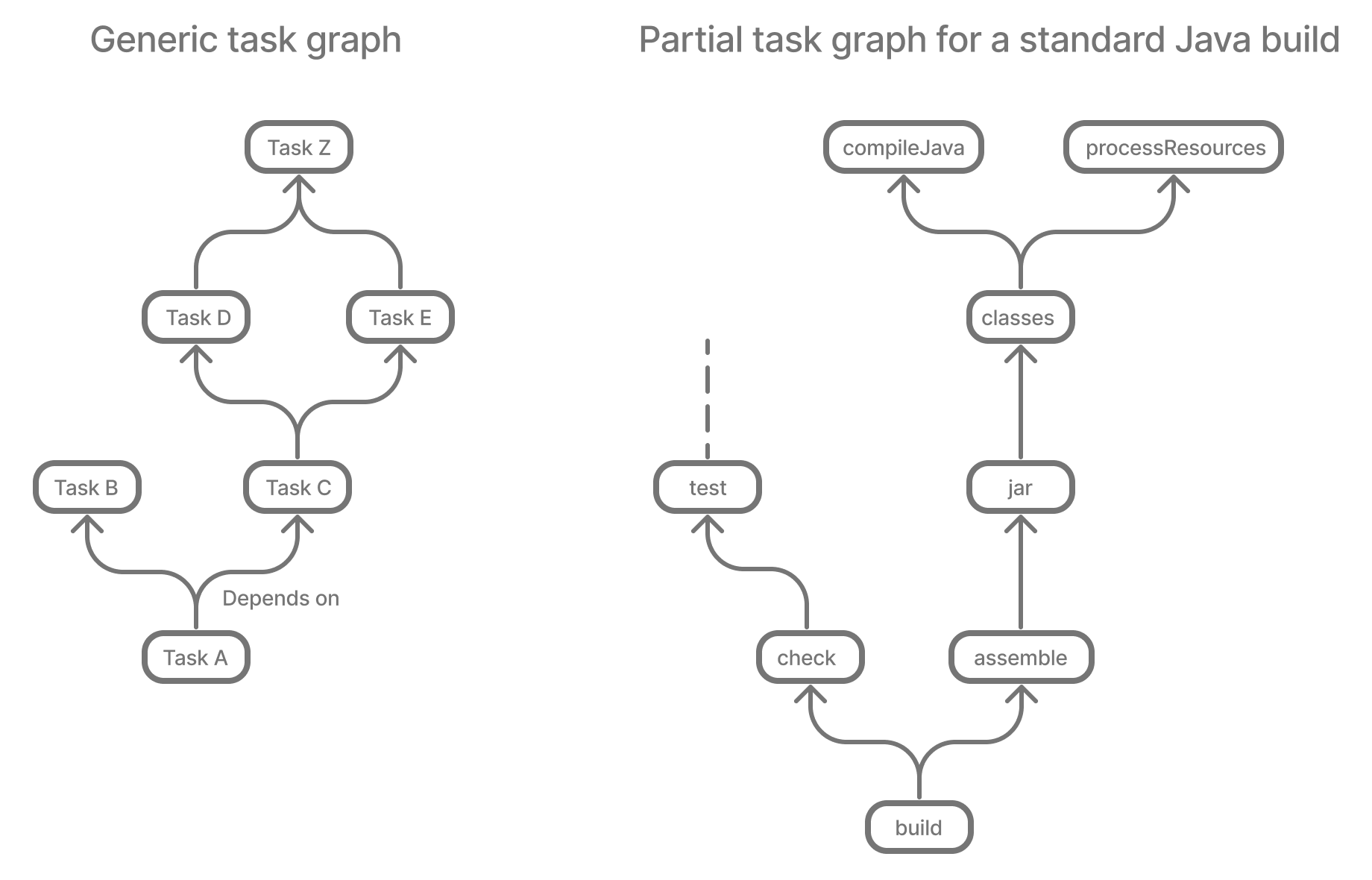
As a build author, you write build logic by defining tasks and declaring how they depend on one another. Gradle uses this information to construct a task graph during the configuration phase that models the relationships between these tasks.
For example, if your project includes tasks such as build, assemble, and createDocs, and you declare that assemble depends on build, and createDocs depends on assemble, Gradle constructs a graph with this order: build → assemble → createDocs.
Gradle builds the task graph before executing any task(s).
Across all projects in the build, tasks form a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG).
This diagram shows two example task graphs, one abstract and the other concrete, with dependencies between tasks represented as arrows:
Hooks into the Gradle Build Lifecycle
Gradle exposes several APIs that allow you to listen to or react to key points in the build lifecycle.
Some APIs let you hook into those phases in init scripts, settings.gradle(.kts) or build.gradle(.kts) to customize or inspect the build as Gradle configures it.
These hooks let you:
-
react to the structure of the build (root + subprojects),
-
configure all projects before their own build scripts are evaluated,
-
debug or collect information during configuration.
Gradle Lifecycle API
The Gradle API accessible via gradle and newer GradleLifecycle API, accessible via gradle.lifecycle, can be used to register actions to be executed at certain points in the build lifecycle:
buildStarted -> DEPRECATED in Gradle 6
└─ beforeSettings
└── settingsEvaluated
└── projectsLoaded
├── beforeProject
├── afterProject
└── projectsEvaluated
└── buildFinished -> DEPRECATED in Gradle 7| # | Hook | Phase | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
Before the |
Early wiring from an init script: global logging/metrics, tweaking |
||
After evaluating |
Adjusting repositories, enabling build scans, reading environment variables, or changing build layout. |
||
After all projects are discovered but before any are configured |
Applying configuration to every project (for example, adding a plugin to all subprojects). |
||
Before each project’s |
Applying defaults, logging project configuration start. |
||
After each project’s |
Validating configuration or detecting missing plugins. |
||
After all projects have been evaluated |
Performing cross-project validation, configuration summaries, or creating aggregated tasks. |
beforeSettings
Where: init script.
When: By the time settings.gradle(.kts) is executing, beforeSettings has already fired.
// 1. beforeSettings: tweak start parameters / log early info
// before the build settings have been loaded and evaluated.
gradle.beforeSettings {
println("[beforeSettings] gradleUserHome = ${gradle.gradleUserHomeDir}")
// Example: default to --parallel if an env var is set
if (System.getenv("CI") == "true") {
println("[beforeSettings] Enabling parallel execution on CI")
gradle.startParameter.isParallelProjectExecutionEnabled = true
} else {
println("[beforeSettings] Disabling parallel execution, not on CI")
gradle.startParameter.isParallelProjectExecutionEnabled = false
}
}// 1. beforeSettings: tweak start parameters / log early info
// before the build settings have been loaded and evaluated.
gradle.beforeSettings {
println("[beforeSettings] gradleUserHome = ${gradle.gradleUserHomeDir}")
// Example: default to --parallel if an env var is set
if (System.getenv("CI") == "true") {
println("[beforeSettings] Enabling parallel execution on CI")
gradle.startParameter.parallelProjectExecutionEnabled = true
} else {
println("[beforeSettings] Disabling parallel execution, not on CI")
gradle.startParameter.parallelProjectExecutionEnabled = false
}
println("")
}settingsEvaluated
Where: settings.gradle(.kts).
When: After the settings file finishes evaluating.
// 2. settingsEvaluated: adjust build layout / repositories / scan config
// when the build settings have been loaded and evaluated.
gradle.settingsEvaluated {
println("[settingsEvaluated] rootProject = ${rootProject.name}")
// Example: enforce a company-wide pluginManagement repo
pluginManagement.repositories.apply {
println("[settingsEvaluated] Ensuring company plugin repo is configured")
mavenCentral()
}
}// 2. settingsEvaluated: adjust build layout / repositories / scan config
// when the build settings have been loaded and evaluated.
gradle.settingsEvaluated { settings ->
println("[settingsEvaluated] rootProject = ${settings.rootProject.name}")
// Example: enforce a company-wide pluginManagement repo
settings.pluginManagement.repositories.with {
println("[settingsEvaluated] Ensuring company plugin repo is configured")
mavenCentral()
}
println("")
}projectsLoaded
Where: settings.gradle(.kts).
When: All projects have been discovered but not yet configured.
// 3. projectsLoaded: we know the full project graph, but nothing configured yet
// to be called when the projects for the build have been created from the settings.
gradle.projectsLoaded {
println("[projectsLoaded] Projects discovered: " + rootProject.allprojects.joinToString { it.name })
// Example: Add a custom property (using the extra properties extension)
allprojects {
println("[projectsLoaded] Setting extra property on ${name}")
extensions.extraProperties["isInitScriptConfigured"] = true
}
}// 3. projectsLoaded: we know the full project graph, but nothing configured yet
// to be called when the projects for the build have been created from the settings.
gradle.projectsLoaded {
println "[projectsLoaded] Projects discovered: " + rootProject.allprojects.collect { it.name }.join(', ')
// Example: Add a custom property (using the extra properties extension)
allprojects {
println("[projectsLoaded] Setting extra property on ${name}")
extensions.extraProperties["isInitScriptConfigured"] = true
}
}beforeProject
Where: build.gradle(.kts) or anywhere you have access to the Gradle instance.
When: For each project as its build script is evaluated.
// to be called immediately before a project is evaluated.
gradle.lifecycle.beforeProject {
println("[lifecycle.beforeProject] Started configuring ${path}")
}
// 4. beforeProject: runs before each build.gradle(.kts) is evaluated
// to be called immediately before a project is evaluated.
gradle.beforeProject {
println("[beforeProject] Started configuring ${path}")
println("[beforeProject] Setup a global build directory for ${name}")
layout.buildDirectory.set(
layout.projectDirectory.dir("build")
)
}// to be called immediately before a project is evaluated.
gradle.lifecycle.beforeProject {
println("[lifecycle.beforeProject] Started configuring ${path}")
}
// 4. beforeProject: runs before each build.gradle(.kts) is evaluated
// to be called immediately before a project is evaluated.
gradle.beforeProject { project ->
println("[beforeProject] Started configuring ${project.path}")
println("[beforeProject] Setup a global build directory for ${project.name}")
project.layout.buildDirectory.set(
project.layout.projectDirectory.dir("build")
)
}afterProject
Where: build.gradle(.kts) or anywhere you have access to the Gradle instance.
When: For each project as its build script is evaluated.
// 5. afterProject: runs after each build.gradle(.kts) is evaluated
// to be called immediately after a project is evaluated.
gradle.afterProject {
println("[afterProject] Finished configuring ${path}")
// Example: apply the Java plugin to all projects that don’t have any plugin yet
if (plugins.hasPlugin("java")) {
println("[afterProject] ${path} already has the java plugin")
} else {
println("[afterProject] Applying java plugin to ${path}")
apply(plugin = "java")
}
}
// to be called immediately after a project is evaluated.
gradle.lifecycle.afterProject {
println("[lifecycle.afterProject] Finished configuring ${path}")
}// 5. afterProject: runs after each build.gradle(.kts) is evaluated
// to be called immediately after a project is evaluated.
gradle.afterProject { project ->
println("[afterProject] Finished configuring ${project.path}")
// Example: apply the Java plugin to all projects that don’t have any plugin yet
if (project.plugins.hasPlugin("java")) {
println("[afterProject] ${project.path} already has the java plugin")
} else {
println("[afterProject] Applying java plugin to ${project.path}")
project.apply(plugin: "java")
}
}
// to be called immediately after a project is evaluated.
gradle.lifecycle.afterProject {
println("[lifecycle.afterProject] Finished configuring ${path}")
}projectsEvaluated
Where: build.gradle(.kts) or anywhere you have access to the Gradle instance.
When: After all projects have been evaluated (i.e., all build.gradle(.kts) files are read and configuration is complete), but before task graph is finalized and before execution starts.
// 6. projectsEvaluated: all projects are fully configured, safe for cross-project checks
// to be called when all projects for the build have been evaluated.
gradle.projectsEvaluated {
println("[projectsEvaluated] All projects evaluated")
// Example: globally configure the java plugin
allprojects {
extensions.findByType<JavaPluginExtension>()?.let { javaExtension ->
if (javaExtension.toolchain.languageVersion.isPresent) {
println("[projectsEvaluated] ${path} uses Java plugin with toolchain ${javaExtension.toolchain.displayName}")
} else {
println("[projectsEvaluated] WARNING: ${path} uses Java plugin but no toolchain is configured, setting Java 17")
javaExtension.toolchain.languageVersion.set(JavaLanguageVersion.of(17))
}
}
}
}// 6. projectsEvaluated: all projects are fully configured, safe for cross-project checks
// to be called when all projects for the build have been evaluated.
gradle.projectsEvaluated {
println("[projectsEvaluated] All projects evaluated")
// Example: globally configure the java plugin
allprojects { project ->
def javaExtension = project.extensions.findByType(JavaPluginExtension)
if(javaExtension) {
if (javaExtension.toolchain.languageVersion.orNull != null) {
println("[projectsEvaluated] ${path} uses Java plugin with toolchain ${javaExtension.toolchain.displayName}")
} else {
println("[projectsEvaluated] WARNING: ${path} uses Java plugin but no toolchain is configured, setting Java 17")
javaExtension.toolchain.languageVersion.set(JavaLanguageVersion.of(17))
}
}
}
}BuildListener API
The legacy BuildListener API is also available.
This listener interface is supported for backward compatibility, but its callbacks have been gradually deprecated as equivalent events became available through the Gradle and GradleLifecycle APIs.
beforeSettings
└── settingsEvaluated
└── projectsLoaded
└── projectsEvaluated
└── taskCompletion
└── buildFinished -> DEPRECATED in Gradle 7BuildListeners are best use to listen to task events using BuildEventsListenerRegistry.onTaskCompletion.
Build Services
You can use the Tooling API’s
OperationCompletionListener.onFinish or implement AutoCloseable in a Build Service and perform cleanup work in its close() method (invoked automatically at build completion).
Flow API
The FlowAction API replaces ad-hoc listeners with a declarative, dependency-aware graph of “flows” which are actions that react to lifecycle transitions and produce well-defined outcomes.