Command-Line Interface Basics
The command-line interface is the primary method of interacting with Gradle outside the IDE.
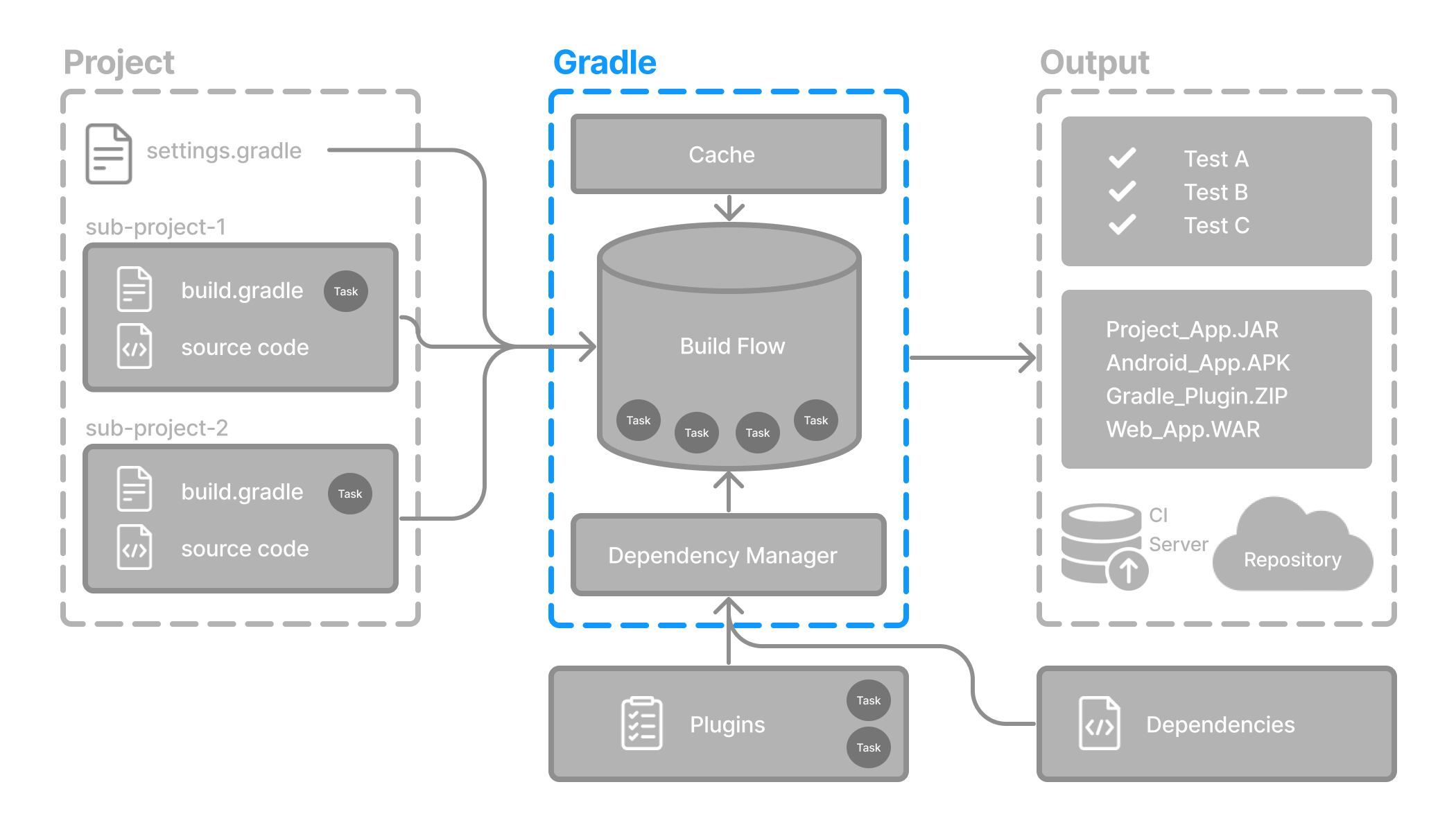
The Gradle CLI is the primary way to interact with a Gradle build from the terminal. You can use it to run tasks, inspect the build, manage dependencies, and control logging, all through flexible and powerful command-line options.
Use of the Gradle Wrapper is highly encouraged. Substitute ./gradlew (in macOS / Linux) or gradlew.bat (in Windows) for gradle in the following examples.
|
Running commands
To execute Gradle commands, use the following simple structure:
gradle [taskName...] [--option-name...]You can specify one or more tasks separated by spaces.
gradle [taskName1 taskName2...] [--option-name...]For example, to run a task named build, simply type:
gradle buildTo clean first, and then build:
gradle clean buildCommand-line options
Gradle commands can include various options to adjust their behavior. Options can appear before or after task names, like so:
gradle [--option-name...] [taskName...]For options that accept a value, use an equals sign (=) for clarity:
gradle [...] --console=plainSome options are toggles and have opposite forms. For instance, to enable or disable the build cache:
gradle build --build-cache
gradle build --no-build-cacheGradle also provides short-option equivalents for convenience. The following two commands are equivalent:
gradle --help
gradle -hExecuting tasks
In Gradle, tasks belong to specific projects.
To clearly indicate which task you want to run, especially in multi-project builds, use a colon (:) as a project separator.
To execute a task named test at the root project level, use:
gradle :testFor nested subprojects, specify the full path using colons:
gradle :subproject:testIf you run a task without any colons, Gradle executes the task in the current directory’s project context:
gradle testTask options
Some tasks accept their own specific options.
Pass these options directly after the task name, prefixed with --.
Here’s how you can pass a custom option:
gradle taskName --exampleOption=exampleValueNext Step: Learn about the Settings file >>