Upgrading within Gradle 9.x.y
This chapter provides the information you need to migrate your Gradle 9.x.y builds to the latest. For migrating to Gradle 9.0.0, see the older migration guide first.
We recommend the following steps for all users:
-
Try running
gradle help --scanand view the deprecations view of the generated Build Scan.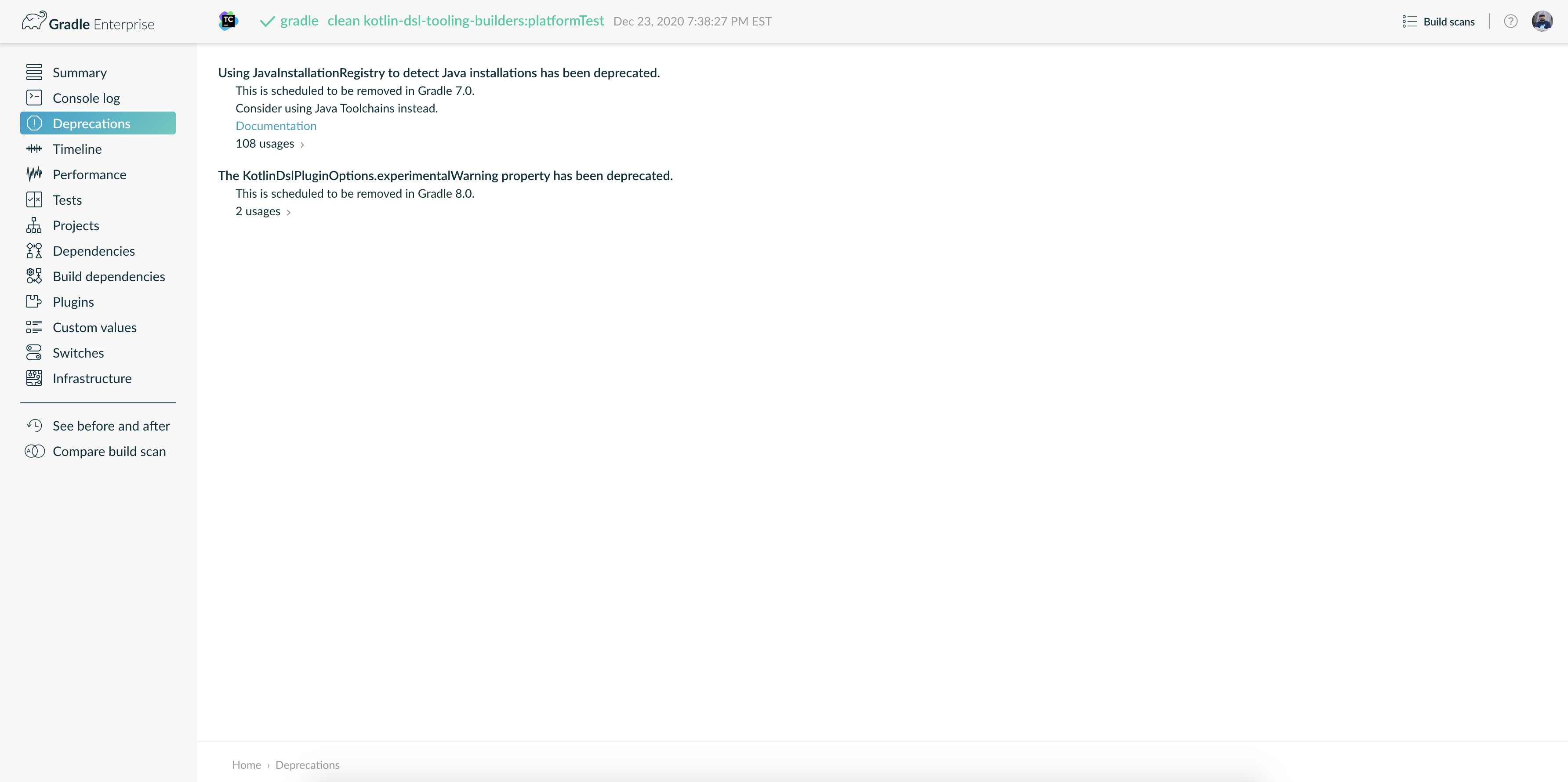
This lets you see any deprecation warnings that apply to your build.
Alternatively, you can run
gradle help --warning-mode=allto see the deprecations in the console, though it may not report as much detailed information. -
Update your plugins.
Some plugins will break with this new version of Gradle because they use internal APIs that have been removed or changed. The previous step will help you identify potential problems by issuing deprecation warnings when a plugin tries to use a deprecated part of the API.
-
Run
gradle wrapper --gradle-version 9.3.1to update the project to 9.3.1. -
Try to run the project and debug any errors using the Troubleshooting Guide.
Upgrading from 9.2.0 and earlier
Potential breaking changes
Referential equality is not guaranteed for Project instances
Instances of Project type representing the same logical Gradle project do not provide any guarantee of being equal by reference (== in Java, === in Kotlin).
However, historically it was possible to observe that such Project instances were exactly the same.
In Gradle 9.3.0, Project instances (for the same logical project) can be different with respect to the referential equality,
even if obtained within the same context, e.g., in the same build script.
This change is necessary to facilitate future performance improvements of Gradle.
The Project.equals() equality behavior remains unchanged.
Avoid referential equality in Kotlin:
// DON'T do this
project.rootProject === project.parentAvoid referential equality in Groovy:
// DON'T do this
project.rootProject.is(project.parent)Avoid referential equality in Java:
MyPlugin.java
// DON'T do this
project.getRootProject() == project.getParent();In general, it is better to check project equality via Project.getPath() or Project.getBuildTreePath() for composite-build support.
The paths are also better suited to be keys in data structures, like maps.
TestNG output may change when using versions before 6.9.13.3
As part of the AbstractTestTask refactoring, Gradle’s integration with TestNG has been updated.
Gradle now relies on a correctly functioning IClassListener to report the hierarchy of test classes and methods.
When using TestNG versions earlier than 6.9.13.3, this can lead to different or degraded output:
-
With older versions, class information may be lost. For example, output that previously looked like:
org.gradle > TestClass > okmay now be reported simply as:ok. -
For TestNG versions from 6.9.10 up to (but not including) 6.9.13.3, the
IClassListenerAPI exists but is broken. This can result in even worse output, such as empty or missing names.
To get correct and stable output, we recommend upgrading to TestNG 6.9.13.3 or newer.
Upgrade to Kotlin 2.2.21
The embedded Kotlin has been upgraded from 2.2.20 to 2.2.21.
Upgrade to ASM 9.9
ASM was upgraded from 9.8 to 9.9 to ensure earlier compatibility for Java 26.
Upgrade to Groovy 4.0.29
Groovy has been updated to 4.0.29.
Upgrade to JaCoCo 0.8.14
JaCoCo has been updated to 0.8.14.
Deprecations
Deprecation of the Wrapper.getAvailableDistributionTypes() method
The method on the Wrapper task has been deprecated and will be removed in Gradle 10.
Use Wrapper.DistributionType.values() to obtain the available distribution types instead.
Deprecation of publishing dependencies on unpublished projects
When publishing a project, Gradle resolves project dependencies to the coordinates of the target project’s publication.
If the target project has no publication, Gradle currently resolves the dependency silently using that project’s group, name, and version.
Starting with Gradle 10, this behavior is deprecated. Gradle will no longer silently ignore the absence of a publication. Publishing a project that depends on another project without a publication will be forbidden and will cause the build to fail. This change prevents publishing broken metadata with dependency coordinates that cannot be resolved.
The example below demonstrates a build that triggers the deprecated behavior:
plugins {
id("java-library")
id("maven-publish")
}
group = "com.example"
version = "1.0.0"
dependencies {
api(project(":other"))
}
publishing {
publications {
create<MavenPublication>("maven") {
from(components["java"])
}
}
}plugins {
id("java-library")
}
group = "com.example"
version = "1.0.0"To avoid this deprecation, ensure that all project dependencies of published projects are also published.
In the example above, applying the maven-publish plugin and configuring a publication in the :other project resolves the issue:
plugins {
id("java-library")
id("maven-publish")
}
group = "com.example"
version = "1.0.0"
publishing {
publications {
create<MavenPublication>("maven") {
from(components["java"])
}
}
}Deprecation of legacy Usage attribute values
Since Gradle 5.6, the Usage attribute has been split into an additional LibraryElements attribute.
In the JVM ecosystem, Usage indicates whether a variant is intended for compilation or runtime, while LibraryElements specifies the format of the artifact (for example, a JAR file or a classes directory).
To ease migration, Gradle has automatically mapped legacy Usage values to their corresponding Usage and LibraryElements pairs:
Legacy |
Replaced |
Replaced |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Starting with Gradle 10, this automatic mapping will no longer occur when legacy Usage values are added directly to an AttributeContainer in build logic.
To maintain backward compatibility for already published modules, Gradle will continue translating legacy Usage values found in published Gradle Module Metadata.
Deprecation of using module coordinates to depend on the current project
Starting with Gradle 10, declaring a dependency on the current project using module coordinates (group, name, version) will no longer resolve to that project.
Instead, Gradle will attempt to resolve that dependency from a repository.
The example below demonstrates the change in behavior:
group = "com.example"
version = "1.0.0"
val deps = configurations.dependencyScope("deps")
val classpath = configurations.resolvable("classpath") {
extendsFrom(deps.get())
attributes.attribute(Category.CATEGORY_ATTRIBUTE, objects.named(Category.LIBRARY))
}
val elements = configurations.consumable("elements") {
attributes.attribute(Category.CATEGORY_ATTRIBUTE, objects.named(Category.LIBRARY))
}
dependencies {
// In Gradle 9.x, this dependency resolves to the `elements` configuration.
// In Gradle 10, this dependency will attempt to resolve from a repository.
deps("com.example:my-project:1.0.0")
}To continue depending on the current project, use a project dependency:
dependencies {
// Declare a dependency on the current project to continue resolving
// to the current project.
deps(project)
}Deprecation of ModuleVersionSelector to ModuleComponentSelector conversion
The conversion of ModuleVersionSelector to ModuleComponentSelector (used in
ResolutionStrategy.force(…),
DependencyResolveDetails.useTarget(Object), and
PluginResolveDetails.useModule(Object)
) has been deprecated and will be removed in Gradle 10.0.0.
Typically, ModuleVersionSelector instances are DependencyContstraint objects.
Note that this deprecation does not apply to ExternalDependency objects, despite them implementing ModuleVersionSelector.
To fix this deprecation, pass one of the supported notations (for example, a String in the group:name:version format).
Upgrading from 9.1.0 and earlier
Potential breaking changes
Upgrade to Kotlin 2.2.20
The embedded Kotlin has been upgraded from 2.2.0 to Kotlin 2.2.20.
Removed incubating ObjectFactory#dependencyCollector() method
The incubating ObjectFactory#dependencyCollector() method has been removed.
You can still create DependencyCollectors within Gradle managed types.
Consumable configurations in bundled plugins are now initialized lazily
Consumable configurations created by bundled Gradle plugins are now initialized only when needed.
Configure actions on these configurations no longer run at configuration time by default.
They only execute if the configuration is published, consumed as a variant, or otherwise realized by build logic.
For example:
plugins {
id("java-library")
}
configurations.named("apiElements").configure {
println("Configuring apiElements")
}With this change, the Configuring apiElements line is no longer printed during configuration time unless apiElements is actually realized.
See Declaring Configurations for more guidance.
ValidatePlugins now has stricter Java version requirements
The ValidatePlugins task must now run on a Java version that is supported by the Gradle daemon.
This change was made because the task depends on several core Gradle services, which may now be compiled to the same bytecode version supported by the daemon.
By default, the task’s convention has been updated:
-
If your project’s toolchain is compatible,
ValidatePluginswill use it. -
Otherwise, it will fall back to the Java version used to run Gradle.
If you explicitly set a toolchain like this:
tasks.withType<ValidatePlugins>().configureEach {
javaLauncher.set(
project.javaToolchains.launcherFor {
languageVersion.set(JavaLanguageVersion.of(17))
}
)
}tasks.withType(ValidatePlugins).configureEach {
javaLauncher.set(
project.javaToolchains.launcherFor {
languageVersion.set(JavaLanguageVersion.of(17))
}
)
}If the specified Java version is not compatible with the Gradle daemon, you must update it to a compatible version.
Deprecations
Deprecation of Project.container(…) methods
The Project.container(…) methods are deprecated and will be removed in Gradle 10.
These methods manually create named domain object containers.
Use a managed property to let Gradle instantiate containers automatically.
If a managed property isn’t possible, use ObjectFactory.domainObjectContainer(…) (available since Gradle 5.5).
Unlike Project.container(Class), the ObjectFactory version decorates container elements and makes them extension aware.
Deprecation of ruleSource-based dependency management APIs
The RuleSource-based dependency management APIs have been deprecated and will be removed in Gradle 10.0.0.
Deprecated APIs include:
Use the alternative methods that accept a ComponentMetadataRule class or an Action.
Deprecation of calling registerFeature without applying the Java plugin
Creating a JVM feature with JavaPluginExtension#registerFeature before applying the Java plugin has been deprecated and will become an error in Gradle 10.0.0.
Ensure the Java plugin is applied before invoking registerFeature.
The following bundled plugins apply the Java plugin automatically:
-
java-library -
application -
groovy -
scala -
war
Upgrading from 9.0.0 and earlier
Potential breaking changes
Upgrade to ASM 9.8
ASM was upgraded from 9.7.1 to 9.8 to ensure earlier compatibility for Java 25.
Upgrade to Groovy 4.0.28
Groovy has been updated to Groovy 4.0.28.
Deprecations
Deprecation of multi-string dependency notation
In an effort to simplify and standardize the Gradle API, the multi-string dependency notation used in dependency management has been deprecated and will no longer be permitted in Gradle 10. Gradle will primarily accept dependency declarations in the form of a single string, with each dependency coordinate separated by a colon.
Below are examples of the deprecated multi-string notation:
dependencies {
implementation(group = "org", name = "foo", version = "1.0")
implementation(group = "org", name = "foo", version = "1.0", configuration = "conf")
implementation(group = "org", name = "foo", version = "1.0", classifier = "classifier")
implementation(group = "org", name = "foo", version = "1.0", ext = "ext")
}
testing.suites.named<JvmTestSuite>("test") {
dependencies {
implementation(module(group = "org", name = "foo", version = "1.0"))
}
}dependencies {
implementation(group: 'org', name: 'foo', version: '1.0')
implementation(group: 'org', name: 'foo', version: '1.0', configuration: 'conf')
implementation(group: 'org', name: 'foo', version: '1.0', classifier: 'classifier')
implementation(group: 'org', name: 'foo', version: '1.0', ext: 'ext')
}
testing.suites.test {
dependencies {
implementation(module(group: 'org', name: 'foo', version: '1.0'))
}
}These declarations should be replaced with the single-string notation:
dependencies {
implementation("org:foo:1.0")
implementation("org:foo:1.0") {
targetConfiguration = "conf"
}
implementation("org:foo:1.0:classifier")
implementation("org:foo:1.0@ext")
}
testing.suites.named<JvmTestSuite>("test") {
dependencies {
implementation("org:foo:1.0")
}
}dependencies {
implementation("org:foo:1.0")
implementation("org:foo:1.0") {
targetConfiguration = "conf"
}
implementation("org:foo:1.0:classifier")
implementation("org:foo:1.0@ext")
}
testing.suites.test {
dependencies {
implementation("org:foo:1.0")
}
}In some cases, a complete single-string notation may not be known up front.
Instead of concatenating the coordinates into a new string, it is possible to use a DependencyFactory to create Dependency instances directly from the individual components:
val group = "org"
val artifactId = "foo"
val version = "1.0"
configurations.dependencyScope("implementation") {
dependencies.add(project.dependencyFactory.create(group, artifactId, version))
}def group = "org"
def artifactId = "foo"
def version = "1.0"
configurations.dependencyScope("implementation") {
dependencies.add(project.dependencyFactory.create(group, artifactId, version))
}Deprecation of ReportingExtension.file(String)
The file() method on ReportingExtension has been deprecated and will be removed in Gradle 10.0.0.
Instead, use ReportingExtension.getBaseDirectory() with file(String) or dir(String).
Deprecation of ReportingExtension.getApiDocTitle()
The getApiDocTitle() method on ReportingExtension has been deprecated and will be removed in Gradle 10.0.0.
There is no direct replacement for this method.
Deprecation of JavaForkOptions.setAllJvmArgs()
The setAllJvmArgs() method on JavaForkOptions and, by inheritance, on JavaExecSpec has been deprecated and will be removed in Gradle 10.0.0.
Instead, to overwrite existing JVM arguments, use:
-
JavaForkOptions.jvmArgs() -
JavaForkOptions.setJvmArgs() -
Provide a
CommandLineArgumentProviderto add arguments viaJavaForkOptions.getJvmArgumentProviders()
Note that setAllJvmArgs() method on JavaForkOptions cleared all fork options before setting jvmArgs.
The properties cleared included:
-
System properties configured via
JavaForkOptions.systemProperties -
JVM argument providers configured via
JavaForkOptions.jvmArgumentProviders -
Argument providers configured via
JavaExecSpec.argumentProviders -
Memory settings configured via
JavaForkOptions.minHeapSizeandJavaForkOptions.maxHeapSize -
All other JVM arguments configured via
JavaForkOptions.jvmArgs -
The assertion and debug flags configured via
JavaForkOptions.enableAssertionsandJavaForkOptions.debug
If the arguments you provide to setJvmArgs() or jvmArgs() depend on any of the above properties being cleared, you will need to manually clear them.
Consider the following snippets for examples of how to implement this change:
plugins {
id("java")
}
tasks.register<JavaExec>("myRunTask") {
jvmArgumentProviders.clear() // Clear existing JVM argument providers
maxHeapSize = null // Clear max heap size
jvmArgs = listOf("-Dfoo", "-Dbar") // Set new JVM arguments
}plugins {
id("java")
}
tasks.named('myRunTask', JavaExec) {
jvmArgumentProviders.clear() // Clear existing JVM argument providers
maxHeapSize = null // Clear max heap size
jvmArgs = ["-Dfoo", "-Dbar"] // Set new JVM arguments
}Deprecation of archives configuration
The archives configuration added by the base plugin has been deprecated and will be removed in Gradle 10.0.0.
Adding artifacts to the archives configuration will now result in a deprecation warning.
If you want the artifact to be built when running the assemble task, add the artifact (or the task that produces it) as a dependency on assemble:
val specialJar = tasks.register<Jar>("specialJar") {
archiveBaseName.set("special")
from("build/special")
}
tasks.named("assemble") {
dependsOn(specialJar)
}Deprecation of the Configuration.visible property
Prior to Gradle 9.0.0, any configuration with isVisible() returning true would implicitly trigger artifact creation when running the assemble task.
This behavior was removed in Gradle 9.0.0, and the Configuration.visible property no longer has any effect.
The property is now deprecated and will be removed in Gradle 10.0.0.
You can safely remove any usage of visible.
If you want the artifacts of a configuration to be built when running the assemble task, add an explicit task dependency on assemble:
val specialJar = tasks.register<Jar>("specialJar") {
archiveBaseName.set("special")
from("build/special")
}
configurations {
consumable("special") {
outgoing.artifact(specialJar)
}
}
tasks.named("assemble") {
dependsOn(specialJar)
}Deprecation of non-string projectProperties in GradleBuild task
The GradleBuild task now deprecates using non-String values in startParameter.projectProperties.
While the type is declared as Map<String, String>, there was no strict enforcement, allowing non-String values to be set.
This deprecated behavior will be removed in Gradle 10.0.0.
If you are using non-String values in project properties, convert them to String representation:
val myIntProp = 42
tasks.register<GradleBuild>("nestedBuild") {
startParameter.projectProperties.put("myIntProp", "$myIntProp") // Convert int to String
}def myIntProp = 42
tasks.register('nestedBuild', GradleBuild) {
startParameter.projectProperties.put('myIntProp', "$myIntProp") // Convert int to String
}Deprecation of project properties for toolchain configuration
In previous versions of Gradle, you could configure toolchains using project properties on the command line with the -P flag.
For example, to disable toolchain auto-detection, you could use -Porg.gradle.java.installations.auto-detect=false.
This behavior is deprecated and will be removed in Gradle 10.0.0.
Instead, you should specify these settings as Gradle properties using the -D flag:
-Dorg.gradle.java.installations.auto-detect=false